
Have you ever looked at a binocular and understood nothing about the numbers printed on it? What Do The Numbers On Binoculars Mean? This article will help you decipher all those measurements!
It is critical for buyers to check out and fully understand all the numbers written on a binocular when shopping for one. However, to those who are going to buy their first binocular, it could seem so overwhelming and confusing.
Fully understanding these specifications will help you choose the best binoculars for your needs and avoid overspending on unnecessary features.
This article will walk you through all the essential numbers you need to know to choose a suitable binocular. Let’s check it out!
First of all, What Is Magnification?
To begin with, magnification is one of the essential features one should take into account. With no exception, all binoculars will have a pair of number such as 10×50 or 7×50.
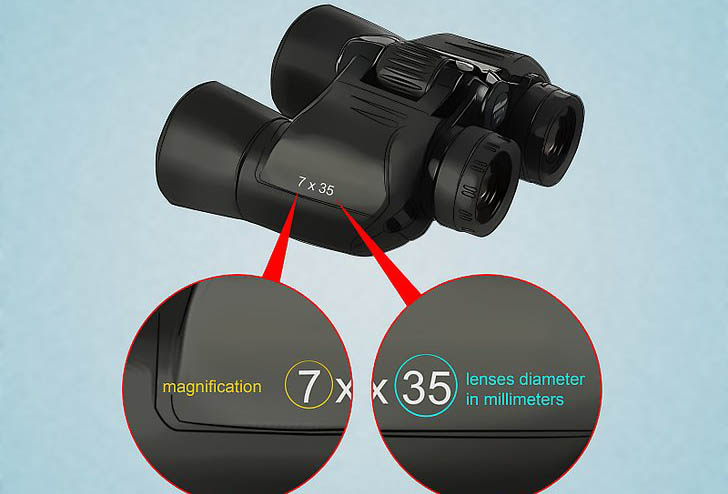

Magnification is described by the first number with the x. It means to which degree the object is enlarged.
For example, 10x50 means that the binocular makes the object look ten times closer than when you look at it with your bare eyes. The higher the magnification, the closer it looks to the object. But the view also gets narrower.
Each magnification is usually used for different purposes. In most cases, binoculars used for wildlife watching in the forest has a magnification of 8x. For larger space, a 10x or even 12x is more prevalent.
And then, Objective Lens Diameter?
The second significant number is the latter number of “10×50“ I have just mentioned above. It implies the diameter of the objective lens. This number is measured in mm. A 10x50 binocular means that it has objective lenses measuring 50mm.
In terms of meaning, the objective lens determines how much light can enter the binocular. The larger objective lenses allow more light to come, which means it can produce a brighter and clearer image, even in low-light conditions.
Binoculars with larger objective lenses are usually quite heavy to backpack on long hikes. The most popular size of objective lenses is 42mm, which is used to watch birds and observe wildlife.
What about the Exit pupil diameter?
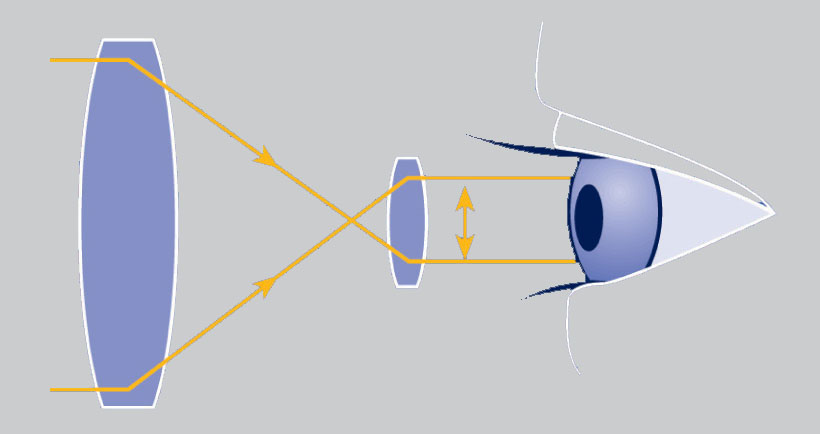
This binocular measurement represents the illuminated circle of light coming from the telescope. This number is calculated by dividing the diameter of the objective by the magnification.
Let’s just say that you have a telescope with a 150 mm and a magnification of 30x, then the exit pupil would be 5mm.

In most cases, it is recommended to choose a larger exit pupil as it can help with eye relief, especially for those who wear glasses. A small exit pupil makes it a lot more challenging to focus on the image.
In normal conditions, the exit pupil should be somewhere around 5mm. Another piece of information you should be aware of is that the eye pupil of human should be higher than that of the exit pupil. Here are the pupil range in some typical cases:
- Bright light: 1-2mm
- Average daylight: 3-4mm
- Dawn or dusk: 5-6mm
- Night or boarding: 7mm
Field of view (FoV) – an Important Number to Understand
Another important binocular number you should know is the field of view (FoV). Simply put, it is the area of the scene you can see using your optic.
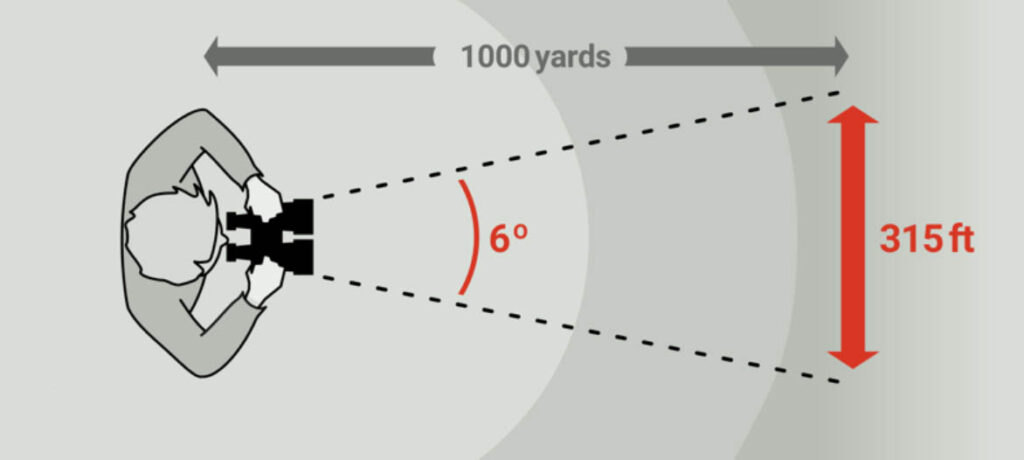
There are many factors determining this number, such as the lens thickness, the eyepiece, the position, and the magnification.
There are also many other design elements; however, to make it easier to understand, in this article, I will leave that part to the manufacturer.
A field of view that is considered wide when it is about 60 degree or more. Thus, choosing a binocular with a wide field of view makes it easier to observe fast-moving objects such as birds or viewing sports.
Each degree is equivalent of 52.5 feet at 1000 yards. For example, a binocular with a 6.5-degree field of view would give you a picture that is around 341.25 feet at 100 yards.
Eye relief
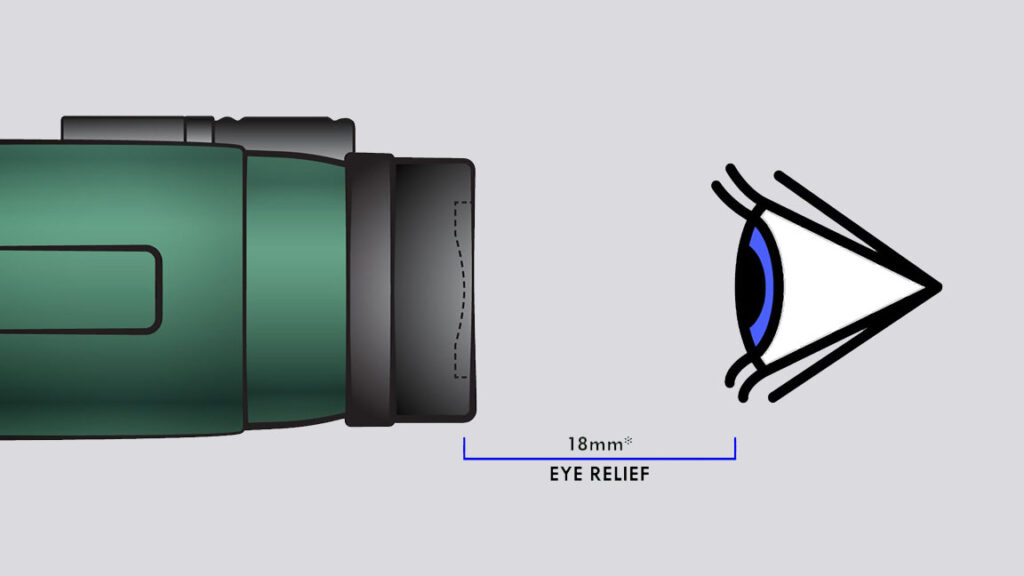
The eye relief is an ideal distance that your eye should be from the eyepiece. That means if you put your eye far away from the eyepiece than the eye relief, the picture seems to lose its edge and the portion you see also gets smaller.
For those who wear glasses, you will need the longer eye relief, and it has to be at least 15mm. A binocular with a long eye relief still does an excellent job for those who do not wear glasses because the eyecups can be easily extended.
Prism System – The core of the Binoculars
Before getting into details about which system of prisms you should go to, let’s first find out the answer to why it needs to be prisms.
Simply put, without a prism, the image you see would be backward and upside down. Prisms help you correct the orientation of the image so that you can view it the right way.
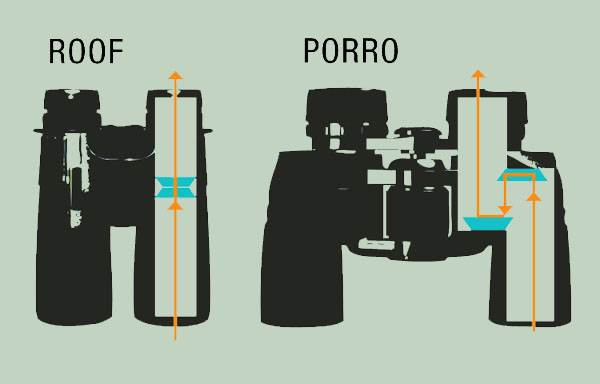
1. Porro Prism
Porro Prism is named after the Italian inventor called Ignazio Porro. It has a much more iconic and traditional design compared to other types of prims. In general, Porro Prism is easier to manufacture and cost a lot less.
- Standard Porro Prism: the standard Porro Prism has offset eyepieces to objective lenses. The most noticeable thing of this type of prism is that the eyepieces are a lot closer together while the lenses are further apart.
- Reverse Porro Prism: this system also has offset eyepieces to lens. However, the eyepieces are further apart, and the lenses are closer together.
2. Roof Prism
Unlike Porro Prism, roof prisms are named for the shape of the assembly. Roof prism designs have a couple of variations such as Amici, Schmidt-Pechan, and Abbe-Koenig.
They all have the same function, which is to allow binoculars to be more compact and narrower than its Porro prism models. If you are wondering about the most significant difference between these two types, the roof prism is a lot more streamlined and more attractive than the other.
Optical Quality
1. Prisms Glasses
I know many of you have heard of the names BK7, BaK-4, and SK-15. But do you know what they are exactly? Keep reading to understand this binocular measurement!
BK7, BaK4, and SK-15 are three basic types of prisms that most people would choose. Let’s take a quick look to find out what each of them is!
- BK7 is made out of borosilicate (crown) glass. It is highly reflective with a refractive rate of about 1.52. BK7 can be used for both Porro prism and roof prism.
- BaK-4 is made out of barium crown. It has a far higher refractive index, which makes the images brighter and well-edged.
- SK-15 is an in-between of the two types mentioned.

2. Types of glasses
ED, HD, FL, HT, what do they exactly mean? Let’s find out!
ED: Extra-low dispersion
This type of lens is known to prevent or at least lessen the chromatic aberration as it provides more options to focus and direct the light. In short, the image produced will be a lot brighter and cleaner.
Most expensive optics will have an ED glass lens as it allows users to take pictures that are clear, sharp with no color fringing.
Some interesting thing about the ED glass:
- ED glass is not so stable when there is a change in temperature. The focal length may change a little bit.
- ED glass also has a low level of refraction, which means it needs curved elements for the same focal length.
HD: High definition
The term HD, surprisingly, is not a type of glass. Instead, it implies the result of the ED lens, which is of high resolution.
FL: Fluoride Lens
This is another version of ED glass, which is classified as a unique and high-quality sub-category.
HT: High Transmission
Just as the title suggests, the lens is well known for its fantastic transmission properties.
3. Chassis Material
For those who do not know, the chassis is the frame of the binocular around the whole optic. In most cases, the chassis is made out of:
Polycarbonate plastic
This is the cheapest material of all. One of the most significant advantages of using Polycarbonate is that it can resist temperature changes. It can hardly be expanded or contract easily when the temperature changes suddenly.
Aluminum
Aluminum is always one of the most popular materials on the market. It is known for being durable, light, and easy to bend. Being naturally corrosion resistant is also a considerable advantage.
Magnesium
The reason why magnesium is used in creating chassis is that it has the strength-to-weight ability. Let’s just imagine that you have to hold the binoculars on your eyes for a long time. The lighter optic will make it a lot less tired for users to keep in such a long time.
That idea has encouraged many manufacturers to use magnesium as it is a lot lighter yet still firm.
4. Glass Coatings
Apart from all the glass elements, prism type and type of glass, glass coatings are also an essential factor that can make the difference. If the coatings are unable to match the prisms, you would not be able to use the binoculars.
So, what are coatings?
For starters, coatings are a kind of formula that allows higher transmission of light-waves into your eyes. In most cases, the way light reaching your eyes depends a lot on how it goes through coatings.
The next question is, how do we classify binocular coatings? There are some basic types as follows:
- Coated (C) Optics: one single anti-reflective coating on at least one lens surface
- Fully Coated (FC) Optics: multiple anti-reflective layers on at least one lens surface
- Multi-Coated (MC) Optics: a single anti-reflective coating on all air-to-glass lens surface
- Fully multi-coated (FMC) Optics: multiple anti-reflective coatings on all air-to-glass surfaces
Next up – Focusing
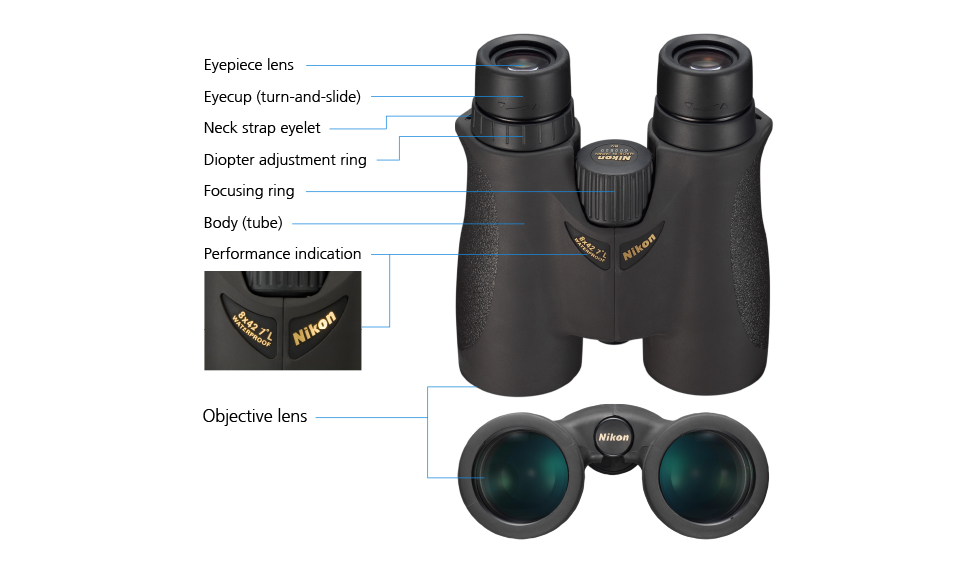
Focusing is another important thing you should spend time understanding when choosing binoculars. To make it easier to follow, let’s first dig deeper into the focus knob.
The focus knob lies between the barrels to help produce more explicit images. However, getting the sharpest focus may take you a lot of time.
To check if you have set the sharpest focus or not, make sure the focus knob is located firmly under your index finger when you hold the binoculars.
Now let’s go deeper into the main part!
I know what you are thinking! How do you focus your binoculars? There are two ways of doing so:
1. Center Focusing (CF)
Center focusing uses a focus knob to focus on the left and right, which will only take a while. The advantage of this method is that it can focus both very close and far away.
2. Individual Focusing (IF)
This method adjusts the focus for each individual eye by rotating the diopter adjustment ring. Once you are done with adjusting, objects from 40 yards to infinity all have a sharp focus.
This way of focusing would be suitable for medium and extended objects, rather than objects within proximity. For example, IF is mostly used in astronomy and marine observation.
3. No Focus/Focus-free
What if you want to individual focus and you will never change it? What if your need is to look at objects only from 40 yards away? No Focus is your solution as the eyepieces are locked and cannot be adjusted.
Diopter Adjustment

There are two common types of dioptre adjustment, as listed below:
- Standard Diopter Adjustment: This is a popular type of dioptre adjustment ring. You can find it on the Porro, and Roof prism binoculars.
- Lockable Diopter Adjustment: It looks quite like the standard version from the left. However, sometimes the lockable ones are used on binoculars with higher spec to make sure the setting will not be changed accidentally.
Special Features
Some binoculars come with some distinctive features such as weatherproofing and gas filled.
Weatherproofing
- A weather-resistant optic: it can withstand the light shower but not in extreme wet condition.
- A weatherproof or waterproof optic: the optic should not let water flow inside.
Gas Filled
To prevent condensation, the binoculars are filled with gases such as nitrogen. It is also useful when there is a need to move binoculars to places that have a temperature difference.
Lastly, Uses, Sizes, and Brands
Uses
- Travel: for traveling purpose, the size and the weight are going to be two of the most important factors to consider. A roof prism would be a lot more convenient to bring with you. It should also come with an objective lens ranging from 32mm to 20mm.
- Hunting: objective lens, in this case, matter more. It would be best if you use binoculars with an objective lens amongst 35mm and 42mm.
- Marine: When it comes to the ocean, a waterproof pair of binoculars is a must. If you want to has a clear view, then choose a magnification of 7x or 8x.
- Astronomy: a large objective lens of 42mm, a tripod, and magnification ranging from 8x to 12x are all you have ever needed in this case. A tripod or a monopod would do a lot of help.
Sizes

Binoculars come in various sizes for different purposes. I have listed a few popular types of binoculars that are chosen by most people.
- Standard Size Binoculars: A standard or full-size binocular for everything from observing wildlife to watching sports
- Compact Binoculars – smaller and lighter – perfect for taking to the theater or concerts or on trips.
- Wide Angle Binoculars – to track fast-moving action across ample space such as wilderness terrain.
Brands

Binocular markets are segmented into three tiers of price: low, medium, and high-end. Here are some suggestion brands for each segmentation:
- Low price: Nikon
- Medium price: Vortex and Pentax
- High-end: Leica, Zeiss, Swarovski
The Last Words,
Choosing binoculars is not an easy task. It has many numbers that you need to spend lots of time researching and understanding. Once you fully understand what you need and what the numbers are about, then choosing a suitable pair of binoculars should not be a problem for you.
Above are all important binocular numbers you should know before making any purchase decision. Hope what I shared gives you some ideas about what you will need from a pair of binoculars. Goodbye!
Vilis-bino
If you want to research more, i think you should read next post: What to Look for When Buying Binoculars?
Referral: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Binoculars
Binocular 101: All basic topics for beginer
